|
Tizen Native API
|
This group provides functions for image objects.
The functions used to create and manipulate image objects are grouped together. They are available to whichever occasion one needs complex imagery on a GUI that could not be achieved by the other Evas' primitive object types, or to make image manipulations.
Evas supports whichever image file types it is compiled with support to (its image loaders) -- check your software packager for that information and see evas_object_image_extension_can_load_get().
Image object basics
The most common use of image objects -- to display an image on the canvas -- is achieved by a common function triplet:
img = evas_object_image_add(canvas); evas_object_image_file_set(img, "path/to/img", NULL); evas_object_image_fill_set(img, 0, 0, w, h);
The first function, naturally, is creating the image object. Then, one must set a source file on it, so that it knows where to fetch image data from. Next, one must set how to fill the image object's area with the given pixel data. One could use just a sub-region of the original image or even have it tiled repeatedly on the image object. For the common case of having the whole source image to be displayed on the image object, stretched to the destination's size, there is also a function helper, to be used instead of evas_object_image_fill_set():
See those functions' documentation for more details.
Scale and resizing
Resizing of image objects scales their respective source images to their areas, if they are set to "fill" the object's area (evas_object_image_filled_set()). If you want any control on the aspect ratio of an image for different sizes, you have to take care of that yourself. There are functions to make images to get loaded scaled (up or down) in memory, already, if you are going to use them at pre-determined sizes and want to save computations.
Evas has even a scale cache, which takes care of caching scaled versions of images with most usage/hits. Finally, you can have images being rescaled smoothly by Evas (more computationally expensive) or not.
Performance hints
When dealing with image objects, there are some tricks to boost the performance of your application, if it does intense image loading and/or manipulations, as in animations on a UI.
Load hints
In image viewer applications, for example, the user is looking at a given image, at full size, and desires that the navigation to the adjacent images on his/her album be fluid and fast. Thus, while displaying a given image, the program can be on the background loading the next and previous images already, so that displaying them on the sequence is just a matter of repainting the screen (and not decoding image data).
Evas addresses this issue with image pre-loading. The code for the situation above would be something like the following:
prev = evas_object_image_filled_add(canvas); evas_object_image_file_set(prev, "/path/to/prev", NULL); evas_object_image_preload(prev, EINA_TRUE); next = evas_object_image_filled_add(canvas); evas_object_image_file_set(next, "/path/to/next", NULL); evas_object_image_preload(next, EINA_TRUE);
If you are loading images which are too big, consider setting its loading size to something smaller, in case you do not expose them in real size. It may speed up the loading considerably:
//To load a scaled down version of the image in memory, if that is //the size you are displaying anyway evas_object_image_load_scale_down_set(img, zoom); //optional: if you know you are going to show a sub-set of the image's //pixels, you can avoid loading the complementary data evas_object_image_load_region_set(img, x, y, w, h);
Refer to Elementary's Photocam widget for a high level (smart) object which does lots of loading speed-ups for you.
Animation hints
If you want to animate image objects on a UI (what you would get by concomitant usage of other libraries, like Ecore and Edje), there are also some tips on how to boost the performance of your application. If the animation involves resizing of an image (thus, re-scaling), you would better turn off smooth scaling on it during the animation, turning it back on afterwards, for less computations. Also, in this case you would better flag the image object in question not to cache scaled versions of it:
evas_object_image_scale_hint_set(wd->img, EVAS_IMAGE_SCALE_HINT_DYNAMIC); // Resizing takes place in between evas_object_image_scale_hint_set(wd->img, EVAS_IMAGE_SCALE_HINT_STATIC);
Finally, movement of opaque images through the canvas is less expensive than of translucid ones, because of blending computations.
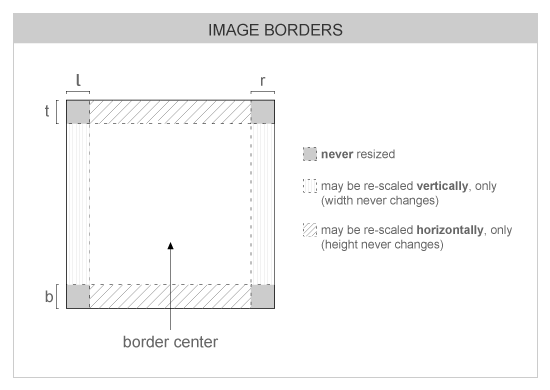
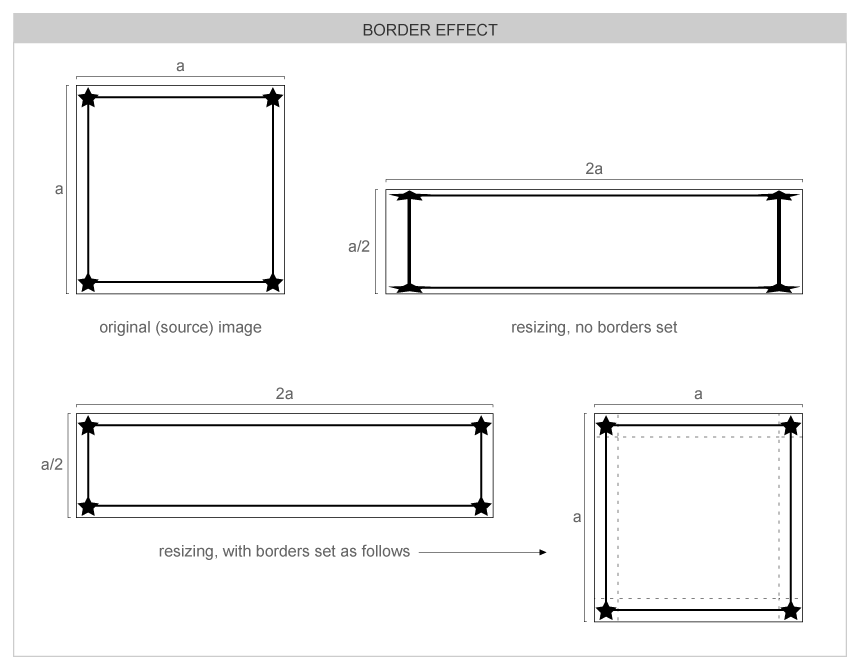
Borders
Evas provides facilities for one to specify an image's region to be treated specially -- as "borders". This makes those regions to be treated specially on resizing scales, by keeping their aspect. This makes setting frames around other objects on UIs easy. See the following figures for a visual explanation:
Manipulating pixels
Evas image objects can be used to manipulate raw pixels in many ways. The meaning of the data in the pixel arrays depends on the image's color space, be warned (see next section). You can set your own data as an image's pixel data, fetch an image's pixel data for saving or altering, convert images between different color spaces and even advanced operations like setting a native surface as image objects' data.
Color spaces
Image objects may return or accept "image data" in multiple formats. This is based on the color space of an object. Here is a rundown on formats:
- EVAS_COLORSPACE_ARGB8888: This pixel format is a linear block of pixels, starting at the top-left row by row until the bottom right of the image or pixel region. All pixels are 32-bit unsigned int with the high-byte being alpha and the low byte being blue in the format ARGB. Alpha may or may not be used by evas depending on the alpha flag of the image, but if not used, should be set to 0xff anyway.
This colorspace uses premultiplied alpha. That means that R, G and B cannot exceed A in value. The conversion from non-premultiplied colorspace is:
R = (r * a) / 255; G = (g * a) / 255; B = (b * a) / 255;
So 50% transparent blue is: 0x80000080. This is not "dark" - just 50% transparent. Values are 0 == black, 255 == solid or full red, green or blue.
- EVAS_COLORSPACE_YCBCR422P601_PL: This is a pointer-list indirected set of YUV (YCbCr) pixel data. This means that the data returned or set is not actual pixel data, but pointers TO lines of pixel data. The list of pointers are first be N rows of pointers to the Y plane - pointing to the first pixel at the start of each row in the Y plane. N is the height of the image data in pixels. Each pixel in the Y, U and V planes is 1 byte exactly, packed. The next N / 2 pointers points to rows in the U plane, and the next N / 2 pointers points to the V plane rows. U and V planes are half the horizontal and vertical resolution of the Y plane.
Row order is top to bottom and row pixels are stored left to right.
There is a limitation that these images MUST be a multiple of 2 pixels in size horizontally or vertically. This is due to the U and V planes being half resolution. Also note that this assumes the itu601 YUV colorspace specification. This is defined for standard television and mpeg streams. HDTV may use the itu709 specification.
Values are0to255, indicating full or no signal in that plane respectively.
- EVAS_COLORSPACE_YCBCR422P709_PL: Not implemented yet.
- EVAS_COLORSPACE_RGB565_A5P: In the process of being implemented in one engine only. This may change.
This is a pointer to image data for 16-bit half-word pixel data in 16bpp RGB 565 format (5 bits red, 6 bits green, 5 bits blue), with the high-byte containing red and the low byte containing blue, per pixel. This data is packed row by row from the top-left to the bottom right.
If the image has an alpha channel enabled there is an extra alpha plane after the color pixel plane. If not, then this data does not exist and should not be accessed in any way. This plane is a set of pixels with 1 byte per pixel defining the alpha values of all pixels in the image from the top-left to the bottom right of the image, row by row. Even though the values of the alpha pixels can be0to255, only values0through to32are used,32being solid and 0 being transparent.
RGB values can be0to31for red and blue and0to63for green, with0being black and31or63being full red, green or blue respectively. This colorspace is also pre-multiplied like EVAS_COLORSPACE_ARGB8888 so:
R = (r * a) / 32; G = (g * a) / 32; B = (b * a) / 32;
- EVAS_COLORSPACE_GRY8: The image is just an alpha mask (8 bits per pixel). This is used for alpha masking.
- Remarks:
- We do not guarantee any proper results if you create an Image object without setting the evas engine.
Functions | |
| Evas_Object * | evas_object_image_add (Evas *e) |
| Creates a new image object on the given Evas e canvas. | |
| Evas_Object * | evas_object_image_filled_add (Evas *e) |
| Creates a new image object that automatically scales its bound image to the object's area, on both axis. | |
| void | evas_object_image_memfile_set (Evas_Object *obj, void *data, int size, char *format, char *key) |
| Sets the data for an image from memory to be loaded. | |
| void | evas_object_image_file_set (Evas_Object *obj, const char *file, const char *key) |
| Sets the source file from where an image object must fetch the real image data (it may be an Eet file, besides pure image ones). | |
| void | evas_object_image_file_get (const Evas_Object *obj, const char **file, const char **key) |
| Gets the source file from where an image object is to fetch the real image data (it may be an Eet file, besides pure image ones). | |
| void | evas_object_image_border_set (Evas_Object *obj, int l, int r, int t, int b) |
| Sets the dimensions for an image object's border, a region which is not scaled together with its center ever. | |
| void | evas_object_image_border_get (const Evas_Object *obj, int *l, int *r, int *t, int *b) |
| Gets the dimensions for an image object's border, a region which is not scaled together with its center ever. | |
| void | evas_object_image_border_center_fill_set (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Border_Fill_Mode fill) |
| Sets how the center part of the given image object (not the borders) should be drawn when Evas is rendering it. | |
| Evas_Border_Fill_Mode | evas_object_image_border_center_fill_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets how the center part of the given image object (not the borders) is to be drawn when Evas is rendering it. | |
| void | evas_object_image_filled_set (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool setting) |
| Sets whether the image object's fill property should track the object's size. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_filled_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Checks whether the image object's fill property should track the object's size. | |
| void | evas_object_image_border_scale_set (Evas_Object *obj, double scale) |
| Sets the scaling factor (multiplier) for the borders of an image object. | |
| double | evas_object_image_border_scale_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the scaling factor (multiplier) for the borders of an image object. | |
| void | evas_object_image_fill_set (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Coord x, Evas_Coord y, Evas_Coord w, Evas_Coord h) |
| Sets how to fill an image object's drawing rectangle given the (real) image bound to it. | |
| void | evas_object_image_fill_get (const Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Coord *x, Evas_Coord *y, Evas_Coord *w, Evas_Coord *h) |
| Sets how an image object is to fill its drawing rectangle, given the (real) image bound to it. | |
| void | evas_object_image_fill_spread_set (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Fill_Spread spread) |
| Sets the tiling mode for the given evas image object's fill. | |
| Evas_Fill_Spread | evas_object_image_fill_spread_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the spread (tiling mode) for the given image object's fill. | |
| void | evas_object_image_size_set (Evas_Object *obj, int w, int h) |
| Sets the size of the given image object. | |
| void | evas_object_image_size_get (const Evas_Object *obj, int *w, int *h) |
| Gets the size of the given image object. | |
| int | evas_object_image_stride_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the row stride of the given image object. | |
| Evas_Load_Error | evas_object_image_load_error_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets a number representing any error that occurred during the last loading of the given image object's source image. | |
| void | evas_object_image_data_set (Evas_Object *obj, void *data) |
| Sets the raw image data of the given image object. | |
| void * | evas_object_image_data_get (const Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool for_writing) |
| Gets a pointer to the raw image data of the given image object. | |
| void * | evas_object_image_data_convert (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Colorspace to_cspace) |
| Converts the raw image data of the given image object to the specified colorspace. | |
| void | evas_object_image_data_copy_set (Evas_Object *obj, void *data) |
| Replaces the raw image data of the given image object. | |
| void | evas_object_image_data_update_add (Evas_Object *obj, int x, int y, int w, int h) |
| Marks a sub-region of the given image object to be redrawn. | |
| void | evas_object_image_alpha_set (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool has_alpha) |
| Enables or disables alpha channel usage on the given image object. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_alpha_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Checks whether alpha channel data is being used on the given image object. | |
| void | evas_object_image_smooth_scale_set (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool smooth_scale) |
| Sets whether to use high-quality image scaling algorithm on the given image object. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_smooth_scale_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Checks whether the given image object is using high-quality image scaling algorithm. | |
| void | evas_object_image_preload (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool cancel) |
| Preloads an image object's image data in the background. | |
| void | evas_object_image_reload (Evas_Object *obj) |
| Reloads an image object's image data. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_save (const Evas_Object *obj, const char *file, const char *key, const char *flags) |
| Saves the given image object's contents to an (image) file. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_pixels_import (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Pixel_Import_Source *pixels) |
| Imports pixels from given source to a given canvas image object. | |
| void | evas_object_image_pixels_get_callback_set (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Object_Image_Pixels_Get_Cb func, void *data) |
| Sets the callback function to get pixels from a canvas' image. | |
| void | evas_object_image_pixels_dirty_set (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool dirty) |
| Sets whether the given image object is dirty and needs to request its pixels. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_pixels_dirty_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Checks whether the given image object is dirty (needs to be redrawn). | |
| void | evas_object_image_load_dpi_set (Evas_Object *obj, double dpi) |
| Sets the DPI resolution of an image object's source image. | |
| double | evas_object_image_load_dpi_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the DPI resolution of a loaded image object in the canvas. | |
| void | evas_object_image_load_size_set (Evas_Object *obj, int w, int h) |
| Sets the load size of a given image object's source image. | |
| void | evas_object_image_load_size_get (const Evas_Object *obj, int *w, int *h) |
| Gets the load size of a given image object's source image. | |
| void | evas_object_image_load_scale_down_set (Evas_Object *obj, int scale_down) |
| Sets the scale down factor of a given image object's source image, when loading it. | |
| int | evas_object_image_load_scale_down_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the scale down factor of a given image object's source image, when loading it. | |
| void | evas_object_image_load_region_set (Evas_Object *obj, int x, int y, int w, int h) |
| Sets a selective region of the source image to load for the given image object. | |
| void | evas_object_image_load_region_get (const Evas_Object *obj, int *x, int *y, int *w, int *h) |
| Gets the coordinates of a given image object's selective (source image) load region. | |
| void | evas_object_image_load_orientation_set (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool enable) |
| Sets whether the orientation information in the image file should be honored. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_load_orientation_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Checks whether the orientation information in the image file should be honored. | |
| void | evas_object_image_colorspace_set (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Colorspace cspace) |
| Sets the colorspace of a given image of the canvas. | |
| Evas_Colorspace | evas_object_image_colorspace_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the colorspace of a given image of the canvas. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_region_support_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the support state of a given image. | |
| void | evas_object_image_native_surface_set (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Native_Surface *surf) |
| Sets the native surface of a given image of the canvas. | |
| Evas_Native_Surface * | evas_object_image_native_surface_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the native surface of a given image of the canvas. | |
| void | evas_object_image_video_surface_set (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Video_Surface *surf) |
| Sets the video surface linked to a given image of the canvas. | |
| const Evas_Video_Surface * | evas_object_image_video_surface_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the video surface linked to a given image of the canvas. | |
| void | evas_object_image_scale_hint_set (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Image_Scale_Hint hint) |
| Sets the scale hint of a given image of the canvas. | |
| Evas_Image_Scale_Hint | evas_object_image_scale_hint_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the scale hint of a given image of the canvas. | |
| void | evas_object_image_content_hint_set (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Image_Content_Hint hint) |
| Sets the content hint setting of a given image object of the canvas. | |
| Evas_Image_Content_Hint | evas_object_image_content_hint_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the content hint setting of a given image object of the canvas. | |
| void | evas_object_image_alpha_mask_set (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool ismask) |
| Enables an image to be used as an alpha mask. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_source_set (Evas_Object *obj, Evas_Object *src) |
| Sets the source object on an image object to used as a proxy. | |
| Evas_Object * | evas_object_image_source_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the current source object of an image object. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_source_unset (Evas_Object *obj) |
| Clears the source object on a proxy image object. | |
| void | evas_object_image_source_visible_set (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool visible) |
| Sets the source object to be visible. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_source_visible_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the state of the source object visibility. | |
| void | evas_object_image_source_clip_set (Evas_Object *obj, Eina_Bool source_clip) |
| Clips the proxy object with the source object's clipper. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_source_clip_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Checks whether an object is clipped by source object's clipper. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_extension_can_load_get (const char *file) |
| Checks whether a file extension is supported by Image Object Functions. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_extension_can_load_fast_get (const char *file) |
| Checks whether a file extension is supported by Image Object Functions. | |
| Eina_Bool | evas_object_image_animated_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Checks whether an image object can be animated (have multiple frames). | |
| int | evas_object_image_animated_frame_count_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the total number of frames of the image object. | |
| Evas_Image_Animated_Loop_Hint | evas_object_image_animated_loop_type_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the kind of looping the image object does. | |
| int | evas_object_image_animated_loop_count_get (const Evas_Object *obj) |
| Gets the number of times the animation of the object loops. | |
| double | evas_object_image_animated_frame_duration_get (const Evas_Object *obj, int start_frame, int fram_num) |
| Gets the duration of a sequence of frames. | |
| void | evas_object_image_animated_frame_set (Evas_Object *obj, int frame_num) |
| Sets the frame to the current frame of an image object. | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef enum _Evas_Colorspace | Evas_Colorspace |
| Enumeration for pixel data of colorspaces supported by Evas. | |
| typedef void(* | Evas_Object_Image_Pixels_Get_Cb )(void *data, Evas_Object *o) |
| Callback of Evas Object Image Pixels. | |
Typedef Documentation
| typedef enum _Evas_Colorspace Evas_Colorspace |
Enumeration for pixel data of colorspaces supported by Evas.
Colorspaces for pixel data supported by Evas
| typedef void(* Evas_Object_Image_Pixels_Get_Cb)(void *data, Evas_Object *o) |
Callback of Evas Object Image Pixels.
Enumeration Type Documentation
| enum _Evas_Colorspace |
Enumeration for pixel data of colorspaces supported by Evas.
- Enumerator:
Function Documentation
| Evas_Object* evas_object_image_add | ( | Evas * | e | ) |
Creates a new image object on the given Evas e canvas.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- If you intend to display an image somehow in a GUI, besides binding it to a real image file or source (with evas_object_image_file_set(), for example), you have to tell this image object how to fill its space with the pixels it can get from the source. See evas_object_image_filled_add(), for a helper on the common case of scaling up an image source to the whole area of the image object.
-
The following is an example:
img = evas_object_image_add(canvas); evas_object_image_file_set(img, "/path/to/img", NULL);
- Parameters:
-
[in] e The given canvas
- Returns:
- The created image object handle
- See also:
- evas_object_image_fill_set()
| Eina_Bool evas_object_image_alpha_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Checks whether alpha channel data is being used on the given image object.
This function returns EINA_TRUE if the image object's alpha channel is being used, or EINA_FALSE otherwise.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- See evas_object_image_alpha_set() for more details.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object
- Returns:
- EINA_TRUE if the alpha channel data is being used,
otherwise EINA_FALSE if the alpha channel data is not being used
| void evas_object_image_alpha_mask_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Eina_Bool | ismask | ||
| ) |
Enables an image to be used as an alpha mask.
This function sets flags, and discard any excess image data not used as an alpha mask.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- Note that there is little point in using a image as alpha mask unless it has an alpha channel.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The object to use as an alpha mask [in] ismask Set EINA_TRUE to use image as alphamask, otherwise EINA_FALSE to not use image as alphamask
| void evas_object_image_alpha_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Eina_Bool | has_alpha | ||
| ) |
Enables or disables alpha channel usage on the given image object.
This function sets a flag on an image object indicating whether or not to use alpha channel data. A value of EINA_TRUE makes it use alpha channel data, and EINA_FALSE makes it ignore that data. Note that this has nothing to do with an object's color as manipulated by evas_object_color_set().
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] has_alpha Set EINA_TRUE to use alpha channel () data,
otherwise set EINA_FALSE to not use it
- See also:
- evas_object_image_alpha_get()
| int evas_object_image_animated_frame_count_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the total number of frames of the image object.
This returns the total number of frames the image object supports (if animated).
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The Image object
- Returns:
- The number of frames
| double evas_object_image_animated_frame_duration_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj, |
| int | start_frame, | ||
| int | fram_num | ||
| ) |
Gets the duration of a sequence of frames.
This function returns the total duration that the specified sequence of frames should take in seconds.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- If you set start_frame to 1 and frame_num 0, you get frame 1's duration. If you set start_frame to 1 and frame_num 1, you get frame 1's duration + frame2's duration.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The Image object [in] start_frame The first frame [in] fram_num The number of frames in the sequence
- Returns:
- The duraction of a sequence of frames.
| void evas_object_image_animated_frame_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| int | frame_num | ||
| ) |
Sets the frame to the current frame of an image object.
This function sets the image object's current frame to frame_num with 1 being the first frame.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] frame_num The index of current frame
| Eina_Bool evas_object_image_animated_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Checks whether an image object can be animated (have multiple frames).
This function returns if the image file of an image object is capable of animation such as an animated gif file might. This is only useful to be called once the image object file has been set.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- The following is an example:
extern Evas_Object *obj; if (evas_object_image_animated_get(obj)) { int frame_count; int loop_count; Evas_Image_Animated_Loop_Hint loop_type; double duration; frame_count = evas_object_image_animated_frame_count_get(obj); printf("This image has %d frames\n",frame_count); duration = evas_object_image_animated_frame_duration_get(obj,1,0); printf("Frame 1's duration is %f. You had better set object's frame to 2 after this duration using timer\n"); loop_count = evas_object_image_animated_loop_count_get(obj); printf("loop count is %d. You had better run loop %d times\n",loop_count,loop_count); loop_type = evas_object_image_animated_loop_type_get(obj); if (loop_type == EVAS_IMAGE_ANIMATED_HINT_LOOP) printf("You had better set frame like 1->2->3->1->2->3...\n"); else if (loop_type == EVAS_IMAGE_ANIMATED_HINT_PINGPONG) printf("You had better set frame like 1->2->3->2->1->2...\n"); else printf("Unknown loop type\n"); evas_object_image_animated_frame_set(obj,1); printf("You set image object's frame to 1. You can see frame 1\n"); }
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The Image object
- Returns:
- EINA_TRUE if obj supports animation,
otherwise EINA_FALSE if it does not support animation
| int evas_object_image_animated_loop_count_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the number of times the animation of the object loops.
This function returns loop count of image. The loop count is the number of times the animation plays fully from first to last frame until the animation should stop (at the final frame).
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- If
0is returned, then looping should happen indefinitely (no limit to the number of times it loops).
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The Image object
- Returns:
- The number of loop of an animated image object
Gets the kind of looping the image object does.
This function returns the kind of looping the image object wants to do.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- If it returns
EVAS_IMAGE_ANIMATED_HINT_LOOP, you should display frames in a sequence like: 1->2->3->1->2->3->1... If it returnsEVAS_IMAGE_ANIMATED_HINT_PINGPONG, it is better to display frames in a sequence like: 1->2->3->2->1->2->3->1... The default type is EVAS_IMAGE_ANIMATED_HINT_LOOP.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The Image object
- Returns:
- The Loop type of the image object
Gets how the center part of the given image object (not the borders) is to be drawn when Evas is rendering it.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object
- Returns:
- fill The fill mode of the center region of obj (a value in Evas_Border_Fill_Mode)
- See also:
- evas_object_image_fill_set()
| void evas_object_image_border_center_fill_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Border_Fill_Mode | fill | ||
| ) |
Sets how the center part of the given image object (not the borders) should be drawn when Evas is rendering it.
This function sets how the center part of the image object's source image is to be drawn, which must be one of the values in Evas_Border_Fill_Mode. By center we mean the complementary part of that defined by evas_object_image_border_set(). This one is very useful for making frames and decorations. You would most probably also be using a filled image (as in evas_object_image_filled_set()) to use as a frame.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] fill The fill mode of the center region of obj (a value in Evas_Border_Fill_Mode)
| void evas_object_image_border_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj, |
| int * | l, | ||
| int * | r, | ||
| int * | t, | ||
| int * | b | ||
| ) |
Gets the dimensions for an image object's border, a region which is not scaled together with its center ever.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- Use
NULLpointers on the border components that you are not interested in: they are ignored by the function.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [out] l The location to store the border's left width in [out] r The location to store the border's right width in [out] t The location to store the border's top width in [out] b The location to store the border's bottom width in
- See also:
- evas_object_image_border_set() for more details.
| double evas_object_image_border_scale_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the scaling factor (multiplier) for the borders of an image object.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object
- Returns:
- The scale factor set for its borders
| void evas_object_image_border_scale_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| double | scale | ||
| ) |
Sets the scaling factor (multiplier) for the borders of an image object.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] scale The scale factor (default is 1.0- i.e. no scaling)
| void evas_object_image_border_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| int | l, | ||
| int | r, | ||
| int | t, | ||
| int | b | ||
| ) |
Sets the dimensions for an image object's border, a region which is not scaled together with its center ever.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- When Evas is rendering, an image source may be scaled to fit the size of its image object. This function sets an area from the borders of the image inwards which is not to be scaled. This function is useful for making frames and for widget theming, where, for example, buttons may be of varying sizes, but their border size must remain constant.
- The units used for l, r, t and b are canvas units.
- The border region itself may be scaled by the evas_object_image_border_scale_set() function.
-
By default, image objects have no borders set, i. e.
l,r,tandbstart as0. -
See the following figures for visual explanation:


- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] l The border's left width [in] r The border's right width [in] t The border's top width [in] b The border's bottom width
| Evas_Colorspace evas_object_image_colorspace_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the colorspace of a given image of the canvas.
This function returns the colorspace of given canvas image.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object pointer
- Returns:
- The colorspace of the image
| void evas_object_image_colorspace_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Colorspace | cspace | ||
| ) |
Sets the colorspace of a given image of the canvas.
This function sets the colorspace of given canvas image.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object pointer [in] cspace The new color space
| Evas_Image_Content_Hint evas_object_image_content_hint_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the content hint setting of a given image object of the canvas.
This function returns the content hint value of the given image of the canvas.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given canvas pointer
- Returns:
- The content hint value set on it
Valid values are define in Evas_Image_Content_Hint.
EVAS_IMAGE_CONTENT_HINT_NONE means an error.
- See also:
- evas_object_image_content_hint_set()
| void evas_object_image_content_hint_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Image_Content_Hint | hint | ||
| ) |
Sets the content hint setting of a given image object of the canvas.
This function sets the content hint value of the given image of the canvas. For example, if you are on the GL engine and your driver implementation supports it, setting this hint to EVAS_IMAGE_CONTENT_HINT_DYNAMIC makes it need zero copies at texture upload time, which is an "expensive" operation.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given canvas pointer [in] hint The content hint value
Valid values are defined in Evas_Image_Content_Hint.
- See also:
- evas_object_image_content_hint_get()
| void* evas_object_image_data_convert | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Colorspace | to_cspace | ||
| ) |
Converts the raw image data of the given image object to the specified colorspace.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- Note that this function does not modify the raw image data. If the requested colorspace is the same as the image colorspace nothing is done and
NULLis returned. You should use evas_object_image_colorspace_get() to check the current image colorspace.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] to_cspace The colorspace to which the image raw data is converted
- See also:
- evas_object_image_colorspace_get
| void evas_object_image_data_copy_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| void * | data | ||
| ) |
Replaces the raw image data of the given image object.
This function lets the application replace an image object's internal pixel buffer with an user-allocated one. For best results, you should generally first call evas_object_image_size_set() with the width and height for the new buffer.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- This call is best suited for when you are using image data with different dimensions than the existing image data, if any. If you only need to modify the existing image in some fashion, then using evas_object_image_data_get() is probably what you are after.
- Note that the caller is responsible for freeing the buffer when finished with it, as user-set image data is not automatically freed when the image object is deleted.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] data The raw data to replace
- See also:
- evas_object_image_data_get()
| void* evas_object_image_data_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Eina_Bool | for_writing | ||
| ) |
Gets a pointer to the raw image data of the given image object.
This function returns a pointer to an image object's internal pixel buffer, for reading only or read/write. If you request it for writing, the image is marked as dirty so that it gets redrawn at the next update.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- Each time you call this function on an image object, its data buffer has an internal reference counter incremented. Decrement it back by using evas_object_image_data_set(). This is specially important for the directfb Evas engine.
- This is best suited for when you want to modify an existing image, without changing its dimensions.
- The contents' format returned by it depend on the color space of the given image object.
- You may want to use evas_object_image_data_update_add() to inform data changes, if you did any.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] for_writing Set EINA_TRUE to set retrieved data as modifiable,
otherwise EINA_FALSE to not set it as modifiable
- Returns:
- The raw image data
- See also:
- evas_object_image_data_set()
| void evas_object_image_data_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| void * | data | ||
| ) |
Sets the raw image data of the given image object.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- Note that the raw data must be of the same size (see evas_object_image_size_set(), which has to be called before this one) and colorspace (see evas_object_image_colorspace_set()) of the image. If data is
NULL, the current image data is freed. Naturally, if one does not set an image object's data manually, it still has one, allocated by Evas.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] data The raw data, or NULL
- See also:
- evas_object_image_data_get()
| void evas_object_image_data_update_add | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| int | x, | ||
| int | y, | ||
| int | w, | ||
| int | h | ||
| ) |
Marks a sub-region of the given image object to be redrawn.
This function schedules a particular rectangular region of an image object to be updated (redrawn) at the next rendering cycle.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] x The X-offset of the region to be updated [in] y The Y-offset of the region to be updated [in] w The width of the region to be updated [in] h The height of the region to be updated
| Eina_Bool evas_object_image_extension_can_load_fast_get | ( | const char * | file | ) |
Checks whether a file extension is supported by Image Object Functions.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- This function is threadsafe.
- Parameters:
-
[in] file The file to check
It should be Eina_Stringshare.
- Returns:
- EINA_TRUE if the file extension is supported,
otherwise EINA_FALSE if it is not supported
| Eina_Bool evas_object_image_extension_can_load_get | ( | const char * | file | ) |
Checks whether a file extension is supported by Image Object Functions.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- If file is a Eina_Stringshare, use evas_object_image_extension_can_load_fast_get directly.
- This function is threadsafe.
- Parameters:
-
[in] file The file to check
- Returns:
- EINA_TRUE if the file extension is supported,
otherwise EINA_FALSE if it is not supported
| void evas_object_image_file_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj, |
| const char ** | file, | ||
| const char ** | key | ||
| ) |
Gets the source file from where an image object is to fetch the real image data (it may be an Eet file, besides pure image ones).
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- You must not modify the strings on the returned pointers.
-
Use
NULLpointers on the file components that you are not interested in: they are ignored by the function.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [out] file The location to store the image file path [out] key The location to store the image key (if file is an Eet one)
| void evas_object_image_file_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| const char * | file, | ||
| const char * | key | ||
| ) |
Sets the source file from where an image object must fetch the real image data (it may be an Eet file, besides pure image ones).
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- If the file supports multiple data stored in it (as Eet files do), you can specify the key to be used as the index of the image in this file.
-
The following is an example:
img = evas_object_image_add(canvas); evas_object_image_file_set(img, "/path/to/img", NULL); err = evas_object_image_load_error_get(img); if (err != EVAS_LOAD_ERROR_NONE) { fprintf(stderr, "could not load image '%s'. error string is \"%s\"\n", valid_path, evas_load_error_str(err)); } else { evas_object_image_fill_set(img, 0, 0, w, h); evas_object_resize(img, w, h); evas_object_show(img); }
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] file The image file path [in] key The image key in file (if its an Eet one),
otherwise setNULL
| void evas_object_image_fill_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Coord * | x, | ||
| Evas_Coord * | y, | ||
| Evas_Coord * | w, | ||
| Evas_Coord * | h | ||
| ) |
Sets how an image object is to fill its drawing rectangle, given the (real) image bound to it.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- Use
NULLpointers on the fill components that you are not interested in: they are ignored by the function.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [out] x The location to store the x coordinate (from the top left corner of the bound image) to start drawing from [out] y The location to store the y coordinate (from the top left corner of the bound image) to start drawing from [out] w The location to store the width the bound image is to be displayed at [out] h The location to store the height the bound image is to be displayed at
See evas_object_image_fill_set() for more details.
| void evas_object_image_fill_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Coord | x, | ||
| Evas_Coord | y, | ||
| Evas_Coord | w, | ||
| Evas_Coord | h | ||
| ) |
Sets how to fill an image object's drawing rectangle given the (real) image bound to it.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- Note that if w or h are smaller than the dimensions of obj, the displayed image is tiled around the object's area. To have only one copy of the bound image drawn, x and y must be
0and w and h need to be the exact width and height of the image object itself, respectively. -
See the following image to better understand the effects of this call. On this diagram, both image object and original image source have
axadimensions and the image itself is a circle, with empty space around it:
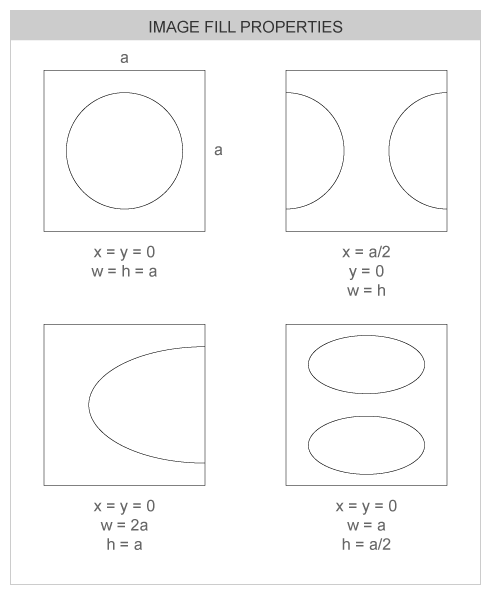
- Remarks:
- The default values for the fill parameters are x = 0, y = 0, w = 0 and h = 0. Thus, if you are not using the evas_object_image_filled_add() helper and want your image displayed, you have to set valid values with this function on your object.
- evas_object_image_filled_set() is a helper function which overrides the values set here automatically, for you, in a given way.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object to operate on [in] x The x coordinate (from the top left corner of the bound image) to start drawing from [in] y The y coordinate (from the top left corner of the bound image) to start drawing from [in] w The width the bound image is displayed at [in] h The height the bound image is displayed at
| Evas_Fill_Spread evas_object_image_fill_spread_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the spread (tiling mode) for the given image object's fill.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given evas image object
- Returns:
- The current spread mode of the image object
| void evas_object_image_fill_spread_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Fill_Spread | spread | ||
| ) |
Sets the tiling mode for the given evas image object's fill.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given evas image object [in] spread One of EVAS_TEXTURE_REFLECT, EVAS_TEXTURE_REPEAT, EVAS_TEXTURE_RESTRICT, or EVAS_TEXTURE_PAD.
Creates a new image object that automatically scales its bound image to the object's area, on both axis.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- This is a helper function around evas_object_image_add() and evas_object_image_filled_set(). It has the same effect of applying those functions in sequence, which is a very common use case.
- Whenever this object gets resized, the bound image is rescaled, too.
- Parameters:
-
[in] e The given canvas
- Returns:
- The created image object handle
| Eina_Bool evas_object_image_filled_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Checks whether the image object's fill property should track the object's size.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object
- Returns:
- EINA_TRUE if it is tracking,
otherwise EINA_FALSE if it is not tracking (and evas_object_fill_set() must be called manually)
- See also:
- evas_object_image_filled_set() for more information
| void evas_object_image_filled_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Eina_Bool | setting | ||
| ) |
Sets whether the image object's fill property should track the object's size.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- If setting is EINA_TRUE, then every evas_object_resize() automatically triggers a call to evas_object_image_fill_set() with the that new size (and
0,0as source image's origin), so the bound image fills the whole object's area.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] setting Set EINA_TRUE to make the fill property follow object size,
otherwise set EINA_FALSE
| double evas_object_image_load_dpi_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the DPI resolution of a loaded image object in the canvas.
This function returns the DPI resolution of the given canvas image.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given canvas pointer
- Returns:
- The DPI resolution of the given canvas image
- See also:
- evas_object_image_load_dpi_set() for more details
| void evas_object_image_load_dpi_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| double | dpi | ||
| ) |
Sets the DPI resolution of an image object's source image.
This function sets the DPI resolution of a given loaded canvas image. This is useful for the SVG image loader.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given canvas pointer [in] dpi The new DPI resolution
- See also:
- evas_object_image_load_dpi_get()
| Evas_Load_Error evas_object_image_load_error_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets a number representing any error that occurred during the last loading of the given image object's source image.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object
- Returns:
- A value giving the last error that occurred
It should be a Evas_Load_Error value. EVAS_LOAD_ERROR_NONE is returned if there is no error.
| Eina_Bool evas_object_image_load_orientation_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Checks whether the orientation information in the image file should be honored.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object pointer
- Returns:
- EINA_TRUE if the orientation information is honored,
otherwise EINA_FALSE if it is not honored
| void evas_object_image_load_orientation_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Eina_Bool | enable | ||
| ) |
Sets whether the orientation information in the image file should be honored.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object pointer [in] enable Set EINA_TRUE to honor the orientation information,
otherwise EINA_FALSE to not honor the orientation information
| void evas_object_image_load_region_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj, |
| int * | x, | ||
| int * | y, | ||
| int * | w, | ||
| int * | h | ||
| ) |
Gets the coordinates of a given image object's selective (source image) load region.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- Use
NULLpointers on the coordinates that you are not interested in: they are ignored by the function.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object pointer [out] x The X-offset of the region to be loaded [out] y The Y-offset of the region to be loaded [out] w The width of the region to be loaded [out] h The height of the region to be loaded
- See also:
- evas_object_image_load_region_get()
| void evas_object_image_load_region_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| int | x, | ||
| int | y, | ||
| int | w, | ||
| int | h | ||
| ) |
Sets a selective region of the source image to load for the given image object.
This function is useful when you are not showing all of an image's area on its image object.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- The image loader for the image format in question has to support selective region loading in order to this function to take effect.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object pointer [in] x The X-offset of the region to be loaded [in] y The Y-offset of the region to be loaded [in] w The width of the region to be loaded [in] h The height of the region to be loaded
- See also:
- evas_object_image_load_region_get()
| int evas_object_image_load_scale_down_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the scale down factor of a given image object's source image, when loading it.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object pointer
- Returns:
- The scale down factor
- See also:
- evas_object_image_load_scale_down_set() for more details
| void evas_object_image_load_scale_down_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| int | scale_down | ||
| ) |
Sets the scale down factor of a given image object's source image, when loading it.
This function sets the scale down factor of a given canvas image. This is useful for the SVG image loader.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object pointer [in] scale_down The scale down factor
| void evas_object_image_load_size_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj, |
| int * | w, | ||
| int * | h | ||
| ) |
Gets the load size of a given image object's source image.
This function gets the geometry size set manually for the given canvas image.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- Use
NULLpointers on the size components that you are not interested in: they are ignored by the function.wandhwill be set with the image's loading size only if the image's load size is set manually: if evas_object_image_load_size_set() has not been called,wandhwill be set with 0.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [out] w The new width of the image's load size that is returned [out] h The new height of the image's load size that is returned
- See also:
- evas_object_image_load_size_set() for more details
| void evas_object_image_load_size_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| int | w, | ||
| int | h | ||
| ) |
Sets the load size of a given image object's source image.
This function sets a new geometry size for the given canvas image. The image will be loaded into memory as if it was the set size instead of the original size.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- The size of a given image object's source image will be less than or equal to the size of
wandh.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given canvas object [in] w The new width of the image's load size [in] h The new height of the image's load size
- See also:
- evas_object_image_load_size_get()
| void evas_object_image_memfile_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| void * | data, | ||
| int | size, | ||
| char * | format, | ||
| char * | key | ||
| ) |
Sets the data for an image from memory to be loaded.
This function is the same as evas_object_image_file_set() but the file to be loaded may exist at an address in memory (the data for the file, not the filename itself). The data at the address is copied and stored for future use, so no data needs to be kept after this call is made. It is managed and freed for you when no longer needed. The size is limited to 2 gigabytes in size, and must be greater than 0. A NULL data pointer is also invalid. Set the filename to NULL to reset to empty state and have the image file data freed from memory using evas_object_image_file_set().
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- The format is optional (pass
NULLif you do not need/use it). It is used to help Evas guess better which loader to use for the data. It may simply be the "extension" of the file as it would normally be on disk such as "jpg", "png", and "gif".
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] data The image file data address [in] size The size of the image file data in bytes [in] format The format of the file (optional),
otherwise setNULL[in] key The image key in file,
otherwise setNULL
| Evas_Native_Surface* evas_object_image_native_surface_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the native surface of a given image of the canvas.
This function returns the native surface of a given canvas image.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given canvas pointer
- Returns:
- The native surface of the given canvas image
| void evas_object_image_native_surface_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Native_Surface * | surf | ||
| ) |
Sets the native surface of a given image of the canvas.
This function sets a native surface of a given canvas image.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given canvas pointer [in] surf The new native surface
| Eina_Bool evas_object_image_pixels_dirty_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Checks whether the given image object is dirty (needs to be redrawn).
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object
- Returns:
- EINA_TRUE if the image is dirty,
otherwise EINA_FALSE if the image is not dirty
| void evas_object_image_pixels_dirty_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Eina_Bool | dirty | ||
| ) |
Sets whether the given image object is dirty and needs to request its pixels.
This function only works properly if a callback for getting pixels has been set.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- Use this function if you really know what you are doing.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] dirty Set EINA_TRUE to mark the image object as dirty,
otherwise set EINA_FALSE to mark the image object as not dirty
| void evas_object_image_pixels_get_callback_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Object_Image_Pixels_Get_Cb | func, | ||
| void * | data | ||
| ) |
Sets the callback function to get pixels from a canvas' image.
This sets a function to be the callback function that gets pixels from an image of the canvas.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given canvas pointer [in] func The callback function [in] data The data pointer to be passed to func
| Eina_Bool evas_object_image_pixels_import | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Pixel_Import_Source * | pixels | ||
| ) |
Imports pixels from given source to a given canvas image object.
This function imports pixels from a given source to a given canvas image.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given canvas object [in] pixels The pixel's source to be imported
- Returns:
- EINA_TRUE if success, otherwise EINA_FALSE.
| void evas_object_image_preload | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Eina_Bool | cancel | ||
| ) |
Preloads an image object's image data in the background.
This function requests the preload of the data image in the background. The work is queued before being processed (because there might be other pending requests of this type).
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- Whenever the image data gets loaded, Evas calls EVAS_CALLBACK_IMAGE_PRELOADED registered callbacks on obj (that may be immediately, if the data is already preloaded before).
- Use EINA_TRUE for cancel on scenarios where you do not need the image data preloaded anymore.
- Any evas_object_show() call after evas_object_image_preload() makes the latter to be cancelled, with the loading process now taking place synchronously (and, thus, blocking the return of the former until the image is loaded). It is highly advisable, then, that the user preload an image with it being hidden, just to be shown on the EVAS_CALLBACK_IMAGE_PRELOADED event's callback.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] cancel Set EINA_FALSE to add to the preloading work queue,
otherwise set EINA_TRUE to remove it (if it is issued before)
| Eina_Bool evas_object_image_region_support_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the support state of a given image.
This function returns the state of the region support of given image
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.2
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object pointer
- Returns:
- The region support state
| void evas_object_image_reload | ( | Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Reloads an image object's image data.
This function reloads the image data bound to image object obj.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object pointer
| Eina_Bool evas_object_image_save | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj, |
| const char * | file, | ||
| const char * | key, | ||
| const char * | flags | ||
| ) |
Saves the given image object's contents to an (image) file.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- The extension suffix on file determines which saver module Evas is to use when saving, thus the final file's format. If the file supports multiple data stored in it (Eet ones), you can specify the key to be used as the index of the image in it.
-
You can specify some flags when saving the image. Currently acceptable flags are
qualityandcompress. Eg.:"quality=100 compress=9"
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] file The filename to be used to save the image (extension obligatory) [in] key The image key in the file (if an Eet one),
otherwiseNULL[in] flags String containing the flags to be used ( NULLfor none)
- Returns:
- EINA_TRUE if the contents are saved successfully,
otherwise EINA_FALSE if it fails
| Evas_Image_Scale_Hint evas_object_image_scale_hint_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the scale hint of a given image of the canvas.
This function returns the scale hint value of the given image object of the canvas.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object pointer
- Returns:
- The scale hint value set on obj
A Evas_Image_Scale_Hint value.
- See also:
- evas_object_image_scale_hint_set() for more details.
| void evas_object_image_scale_hint_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Image_Scale_Hint | hint | ||
| ) |
Sets the scale hint of a given image of the canvas.
This function sets the scale hint value of the given image object in the canvas, which affects how Evas is to cache scaled versions of its original source image.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object pointer [in] hint The scale hint
A Evas_Image_Scale_Hint value.
- See also:
- evas_object_image_scale_hint_get()
| void evas_object_image_size_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj, |
| int * | w, | ||
| int * | h | ||
| ) |
Gets the size of the given image object.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [out] w The location to store the width of the image in, or NULL[out] h The location to store the height of the image in, or NULL
See evas_object_image_size_set() for more details.
| void evas_object_image_size_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| int | w, | ||
| int | h | ||
| ) |
Sets the size of the given image object.
This function scales down or crops the image so that it is treated as if it were at the given size. If the size given is smaller than the image, it is cropped. If the size given is larger, then the image is treated as if it were in the upper left hand corner of a larger image that is otherwise transparent.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] w The new width of the image [in] h The new height of the image
| Eina_Bool evas_object_image_smooth_scale_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Checks whether the given image object is using high-quality image scaling algorithm.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object
- Returns:
- EINA_TRUE if smooth scale is being used,
otherwise EINA_FALSE if smooth scale is not being used
- See also:
- evas_object_image_smooth_scale_set()
| void evas_object_image_smooth_scale_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Eina_Bool | smooth_scale | ||
| ) |
Sets whether to use high-quality image scaling algorithm on the given image object.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- When enabled, a higher quality image scaling algorithm is used when scaling images to sizes other than the source image's original one. This gives better results but is more computationally expensive.
- Image objects get created originally with smooth scaling on.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object [in] smooth_scale Set EINA_TRUE to use smooth scale,
otherwise set EINA_FALSE to not use it
- See also:
- evas_object_image_smooth_scale_get()
| Eina_Bool evas_object_image_source_clip_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Checks whether an object is clipped by source object's clipper.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.8
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The proxy (image) object
- Returns:
- EINA_TRUE if source clip is enabled, otherwise EINA_FALSE if source clip is not enabled
| void evas_object_image_source_clip_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Eina_Bool | source_clip | ||
| ) |
Clips the proxy object with the source object's clipper.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.8
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The proxy (image) object [in] source_clip Set EINA_TRUE if obj must be clipped by the source clipper,
otherwise set EINA_FALSE
| Evas_Object* evas_object_image_source_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the current source object of an image object.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The Image object
- Returns:
- The source object (if any),
otherwiseNULLif not in "proxy mode" or on errors
- See also:
- evas_object_image_source_set() for more details
| Eina_Bool evas_object_image_source_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Object * | src | ||
| ) |
Sets the source object on an image object to used as a proxy.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- If an image object is set to behave as a proxy, it mirrors the rendering contents of a given source object in its drawing region, without affecting that source in any way. The source must be another valid Evas object. Other effects may be applied to the proxy, such as a map (see evas_object_map_set()) to create a reflection of the original object (for example).
-
Any existing source object on obj is removed after this call. Setting src to
NULLclears the proxy object (not in "proxy state" anymore). - You cannot set a proxy as another proxy's source.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The proxy (image) object [in] src The source object to use for the proxy
- Returns:
- EINA_TRUE if the source object is set successfully,
otherwise EINA_FALSE on error
Clears the source object on a proxy image object.
This function is equivalent to calling evas_object_image_source_set() with a NULL source.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The Image object to clear source of
- Returns:
- EINA_TRUE if the source object is cleared successfully,
otherwise EINA_FALSE on error
| Eina_Bool evas_object_image_source_visible_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the state of the source object visibility.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.8
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The proxy (image) object
- Returns:
- EINA_TRUE if source object is visible,
otherwise EINA_FALSE
| void evas_object_image_source_visible_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Eina_Bool | visible | ||
| ) |
Sets the source object to be visible.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.8
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- If visible is set to EINA_FALSE, the source object of the proxy (obj) is invisible.
- This function works differently to evas_object_show() and evas_object_hide(). Once the source object is hidden by evas_object_hide() then the proxy object is hidden as well. Actually in this case both objects are excluded from the Evas internal update circle.
- Using this method, you can toggle the visibility of a proxy's source object keeping the proxy visibility untouched.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The proxy (image) object [in] visible Set EINA_TRUE to show the source object,
otherwise set EINA_FALSE to not show it
| int evas_object_image_stride_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the row stride of the given image object.
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Remarks:
- The row stride is the number of bytes between the start of a row and the start of the next row for image data.
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given image object
- Returns:
- The stride of the image (in bytes)
| const Evas_Video_Surface* evas_object_image_video_surface_get | ( | const Evas_Object * | obj | ) |
Gets the video surface linked to a given image of the canvas.
This function returns the video surface linked to a given canvas image.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given canvas pointer
- Returns:
- The video surface of the given canvas image
| void evas_object_image_video_surface_set | ( | Evas_Object * | obj, |
| Evas_Video_Surface * | surf | ||
| ) |
Sets the video surface linked to a given image of the canvas.
This function links a video surface to a given canvas image.
- Since (EFL) :
- 1.1
- Since :
- 2.3.1
- Parameters:
-
[in] obj The given canvas pointer [in] surf The new video surface